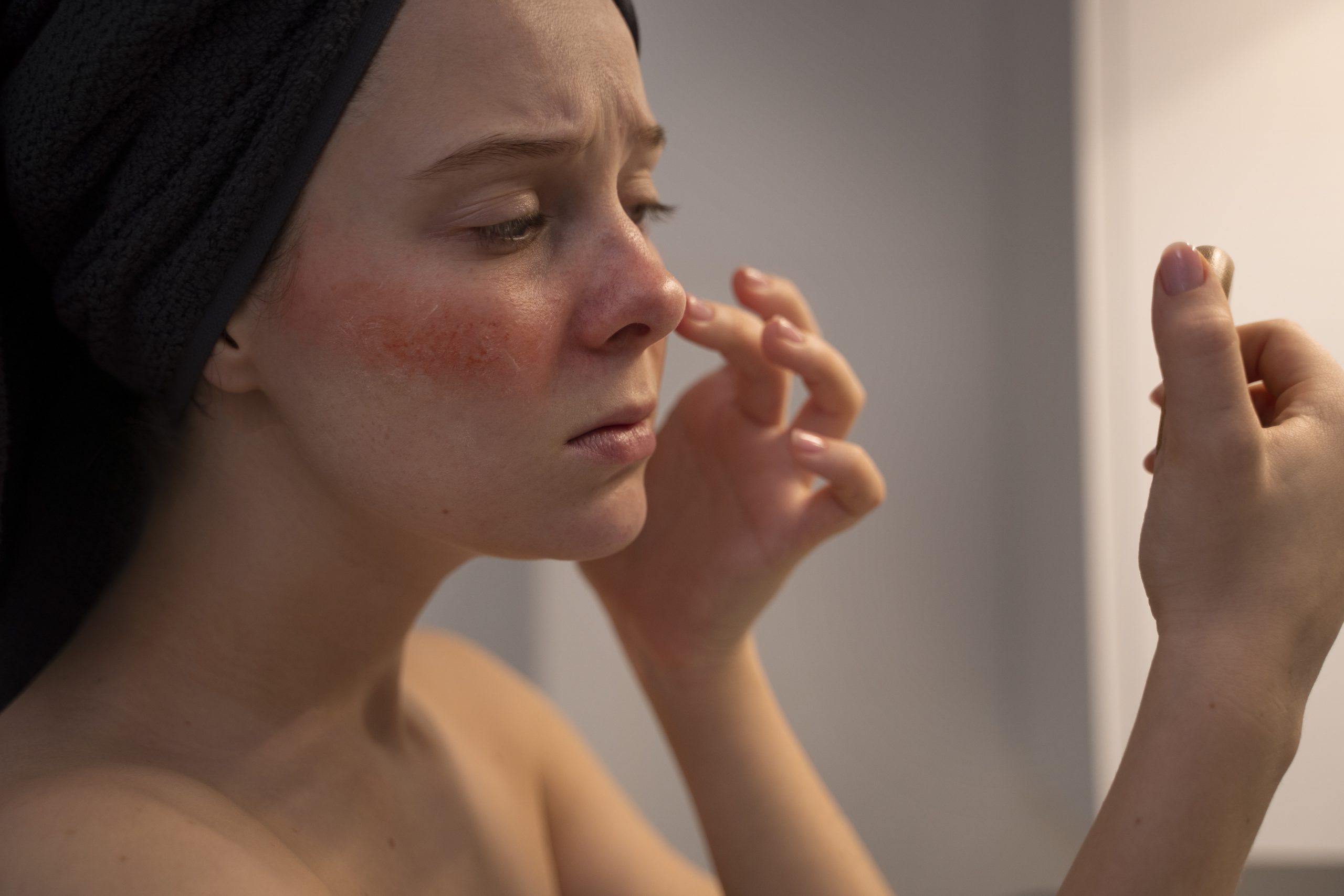
Skin sensitivities refer to a range of reactions that the skin may have when it encounters certain substances or environmental factors. These reactions can vary widely in severity and may manifest as redness, itching, burning, stinging, swelling, or other discomfort. Skin sensitivities can be temporary or chronic, and they can affect individuals of all ages and skin types.
There are several types of skin sensitivities, including:
- Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an irritant or allergen, leading to inflammation. Irritant contact dermatitis is more common and occurs when the skin reacts to substances like soaps, detergents, or chemicals. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin has an allergic reaction to a specific substance, such as certain metals, fragrances, or latex.
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often runs in families and is associated with other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever.
- Urticaria (Hives): Hives are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can be triggered by allergic reactions, medications, infections, or other factors. They typically appear suddenly and may come and go over a few hours to days.
- Rosacea: While not always classified as a skin sensitivity, rosacea involves increased skin sensitivity and can cause redness, flushing, and inflammation of the face.
- Photoallergic and Phototoxic Reactions: Some individuals may experience skin reactions when exposed to sunlight, either due to an allergic reaction (photoallergic) or due to the interaction between sunlight and certain substances applied to the skin (phototoxic).
- Neurogenic Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience increased skin sensitivity due to neurological factors, such as nerve damage or disorders like fibromyalgia or neuropathy.
- Sensitive Skin Syndrome: This is a term used to describe individuals who have skin that is more prone to react to various factors, such as skincare products, weather changes, or stress. Sensitive skin may be influenced by genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices.
Managing skin sensitivities often involves identifying and avoiding triggers, using gentle skincare products, maintaining proper hydration and moisturization, protecting the skin from environmental factors, and seeking medical advice if symptoms persist or worsen.